How to operate a drone? This seemingly simple question opens a world of exciting possibilities, from breathtaking aerial photography to precision surveying. But mastering drone operation requires more than just pushing buttons; it demands a thorough understanding of safety regulations, pre-flight procedures, and skillful control. This guide will equip you with the knowledge and confidence to navigate the skies responsibly and capture stunning visuals, all while adhering to legal guidelines and best practices.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Successfully navigating the airspace requires a solid grasp of regulations and safe flying practices. For a comprehensive guide covering all aspects, including practical tips and safety procedures, you should consult this excellent resource on how to operate a drone before your first flight.
This will ensure you’re well-prepared and confident in handling your drone responsibly.
We’ll cover everything from understanding international drone regulations and performing essential pre-flight checks to mastering drone controls, capturing stunning aerial footage, and troubleshooting common issues. We’ll also delve into advanced techniques and maintenance procedures to ensure the longevity of your drone and your safety.
Drone Regulations and Safety
Operating a drone responsibly requires understanding and adhering to local regulations and prioritizing safety. This section details legal requirements, airspace restrictions, and crucial safety procedures for pre-flight, in-flight, and post-flight operations. Failure to comply with regulations can result in significant penalties, including fines and legal action.
Drone Regulations by Country
Drone regulations vary significantly across countries. Understanding these differences is crucial for safe and legal operation. The following table provides a comparison of regulations in three countries, but it is essential to consult the specific regulations of the country where you plan to fly.
| Country | Licensing Requirements | Airspace Restrictions | Penalties for Violations |
|---|---|---|---|
| United States | Registration required for most drones; specific licenses may be needed for commercial operations. | Restrictions near airports, sensitive infrastructure, and populated areas; specific no-fly zones are enforced. | Fines, grounding of the drone, and potential legal action. |
| Canada | Registration and licensing requirements depend on drone weight and intended use (recreational or commercial). | Similar restrictions to the US, with designated no-fly zones near airports and sensitive areas. | Fines, drone seizure, and potential legal prosecution. |
| United Kingdom | Registration is mandatory; operator competency is assessed for commercial operations. | Strict regulations around airports and other sensitive locations; height restrictions apply. | Significant fines and potential legal consequences. |
Pre-Flight Safety Procedures
A thorough pre-flight checklist is paramount for safe drone operation. This ensures the drone is in optimal condition and minimizes the risk of accidents or malfunctions.
- Inspect the drone for any physical damage.
- Check battery levels and ensure they are fully charged.
- Calibrate the compass and GPS to ensure accurate positioning.
- Review weather conditions and avoid flying in strong winds or adverse weather.
- Check the airspace for any restrictions in your flight area.
- Inform others in the area of your intended flight path.
Post-Flight Procedures
Post-flight procedures are equally important to ensure the drone’s safety and longevity. These steps help maintain the drone’s functionality and prevent future issues.
- Carefully land the drone in a safe, designated area.
- Inspect the drone for any damage sustained during the flight.
- Properly store the drone and its components to protect them from damage.
- Download and review flight data to analyze performance and identify any potential issues.
- Clean the drone to remove any debris or dirt.
Pre-Flight Checklist and Preparation

A comprehensive pre-flight checklist is crucial for a successful and safe drone flight. This includes verifying the drone’s condition, checking battery levels, and calibrating the drone’s navigational systems.
Pre-Flight Checklist
This flowchart visually represents the pre-flight steps. Each step should be carefully followed to ensure a safe flight.
Flowchart (Textual Representation):
Start –> Inspect Drone –> Check Batteries –> Calibrate Compass/GPS –> Check Weather –> Check Airspace Restrictions –> Notify Others –> Proceed to Takeoff –> End
Battery Management and Charging
Proper battery management is essential for safe and extended drone use. This involves using the correct charger, storing batteries appropriately, and monitoring their condition.
- Always use the manufacturer’s recommended charger.
- Store batteries in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight.
- Monitor battery voltage and replace batteries that show signs of wear or damage.
- Avoid overcharging or discharging batteries.
Compass and GPS Calibration
Calibrating the drone’s compass and GPS ensures accurate flight data and prevents unexpected behavior. This is particularly important before the first flight and after any potential impact.
- Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for compass calibration, typically involving rotating the drone in a figure-eight pattern.
- Ensure the drone has a clear view of the sky for optimal GPS signal acquisition.
- Perform calibration in an open area, away from electromagnetic interference.
Taking Off and Landing
Safe takeoff and landing procedures are critical for preventing accidents and damage. This section Artikels techniques for various conditions and environments.
Safe Takeoff and Landing Procedures
The following steps provide a guide for a smooth and safe landing.
- Select a level, clear area for takeoff and landing.
- Ensure the drone’s propellers are clear of obstacles.
- Initiate takeoff slowly and steadily, monitoring the drone’s altitude and stability.
- Maintain visual contact with the drone at all times.
- For landing, gradually reduce altitude and speed, ensuring a gentle touchdown.
- Power down the drone after landing.
Takeoff and Landing in Challenging Environments
Windy conditions and uneven terrain present unique challenges. Adapting takeoff and landing techniques is crucial for safety.
Successfully piloting a drone involves understanding its controls and adhering to safety regulations. Learning the basics, from pre-flight checks to maneuvering in various conditions, is crucial. For a comprehensive guide covering all aspects, check out this excellent resource on how to operate a drone which provides valuable insights for both beginners and experienced users. Mastering the art of drone operation ensures safe and effective flights.
- In windy conditions, choose a sheltered location and consider using a weighted base for increased stability.
- On uneven terrain, select a flat, stable surface for takeoff and landing to prevent tipping or damage.
- Always prioritize safety over attempting a flight in extremely challenging conditions.
Drone Controls and Navigation
Understanding drone controls and navigation is essential for safe and effective operation. This section covers basic controls, different control schemes, and strategies for overcoming navigation challenges.
Basic Drone Controls
Most drones utilize joysticks or app-based controls for navigation. Joysticks provide precise control, while app-based controls offer a more intuitive interface for beginners. Understanding the functions of each control is crucial for safe and effective flight.
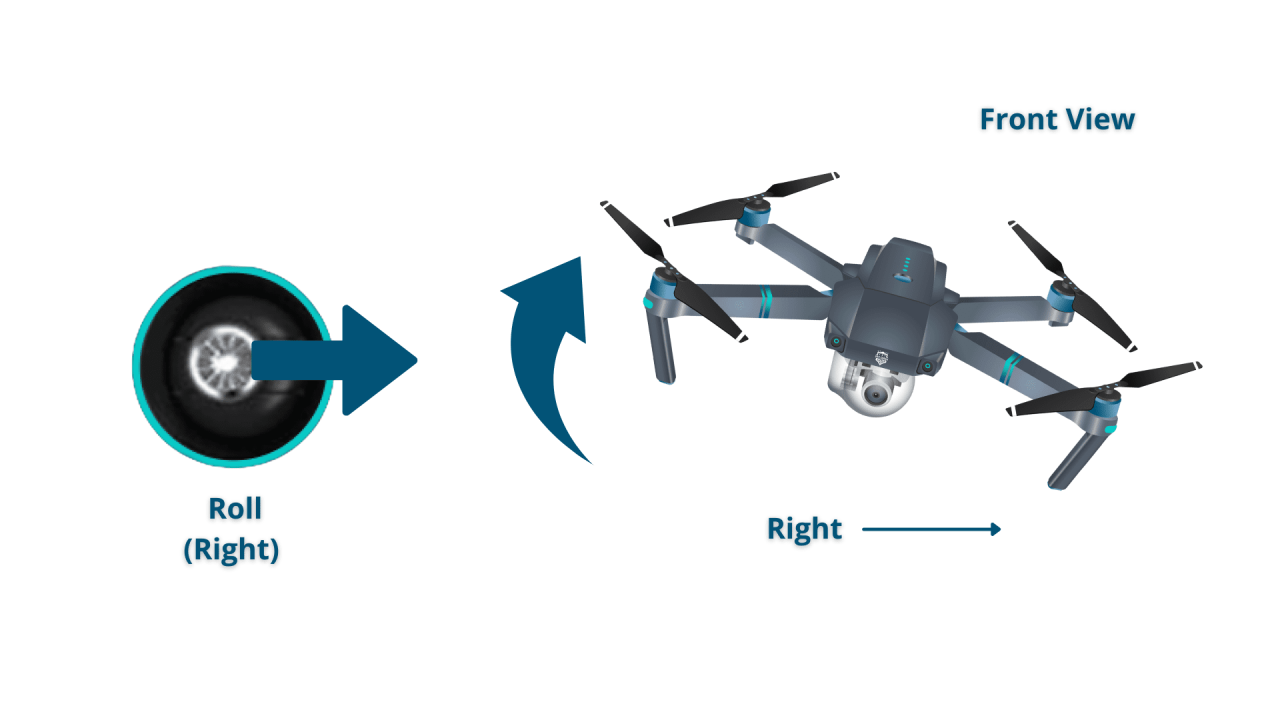
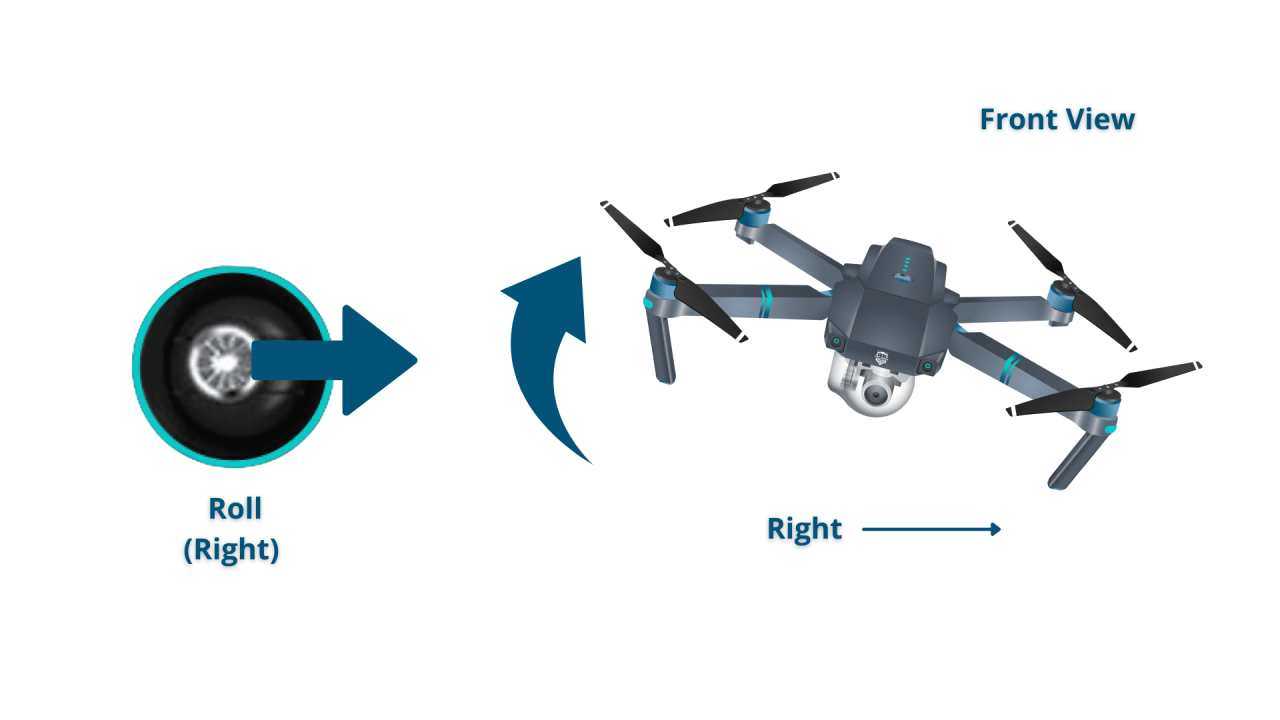
- Left Joystick: Controls yaw (rotation) and throttle (altitude).
- Right Joystick: Controls pitch (forward/backward) and roll (left/right).
- Buttons/Switches: Used for various functions such as camera control, return-to-home, and emergency stop.
Navigation Challenges and Strategies
Several factors can impact drone navigation, including GPS signal loss, wind, and obstacles. Effective strategies are crucial for safe flight.
- GPS Signal Loss: Maintain a clear view of the sky for optimal GPS reception. Consider flying in areas with strong GPS signals.
- Wind: Adjust the drone’s controls to compensate for wind gusts. Avoid flying in strong winds.
- Obstacles: Plan your flight path carefully to avoid obstacles. Utilize the drone’s obstacle avoidance features (if available).
Advanced Maneuvers
Advanced maneuvers, such as precise hovering and circling, require practice and skill. These techniques enhance the drone’s capabilities for photography and videography.
- Precise Hovering: Requires fine-tuning the throttle to maintain a steady altitude.
- Circling: Involves coordinated use of yaw and roll to create smooth, controlled circles.
Drone Camera Operation and Photography
Drone cameras offer unique perspectives and capabilities for capturing stunning aerial footage. Understanding camera features, settings, and techniques is crucial for high-quality results.
Drone Camera Features and Settings
Drone cameras typically offer a range of features and settings, allowing for customization to various shooting conditions and styles.
- Resolution: Determines the image quality (e.g., 4K, 1080p).
- Frame Rate: Affects the smoothness of video (e.g., 24fps, 30fps, 60fps).
- Aperture: Controls the amount of light entering the camera, affecting depth of field.
- ISO: Adjusts the camera’s sensitivity to light, impacting image noise.
- Shutter Speed: Controls the duration the camera’s sensor is exposed to light.
Camera Modes and Applications
| Mode | Description | Ideal Conditions | Example Shot |
|---|---|---|---|
| Photo | Captures still images. | Bright, sunny conditions; landscapes, architecture. | High-resolution image of a mountain range. |
| Video | Records moving images. | Various conditions; dynamic scenes, events. | Smooth, cinematic footage of a city skyline. |
| Time-lapse | Captures a series of images over time, creating a condensed video. | Scenic locations with slow-changing conditions; clouds, sunsets. | Time-lapse of clouds moving across the sky. |
| Panorama | Stitches multiple images together to create a wide-angle shot. | Landscapes, cityscapes; wide-open spaces. | Panoramic view of a coastline. |
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Drone malfunctions can occur, but understanding common problems and their solutions can minimize downtime and prevent costly repairs. This section details troubleshooting steps for common issues.
Common Drone Malfunctions and Troubleshooting, How to operate a drone

This troubleshooting guide Artikels steps to resolve common problems.
Flowchart (Textual Representation):
Problem –> Low Battery? –> Yes: Charge Battery –> No: GPS Signal Loss? –> Yes: Check GPS Signal, Recalibrate –> No: Motor Failure? –> Yes: Inspect Motors, Replace if Necessary –> No: Other Issues? –> Consult Manual/Manufacturer
Preventative Maintenance
Regular maintenance extends the lifespan of the drone and minimizes the risk of malfunctions.
- Clean the drone regularly to remove dirt and debris.
- Inspect propellers for damage and replace as needed.
- Store the drone in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight.
- Check and tighten screws periodically.
Drone Maintenance and Storage
Proper maintenance and storage are crucial for preserving the drone’s functionality and longevity. This section Artikels cleaning procedures, essential tools, and safe storage practices.
Drone Cleaning and Maintenance
Regular cleaning and maintenance are essential to prevent damage and ensure optimal performance.
- Use a soft cloth to gently wipe down the drone body and propellers.
- Avoid using harsh chemicals or abrasive materials.
- Inspect the drone for any loose parts or damage.
- Lubricate moving parts as needed (refer to the manufacturer’s instructions).
Essential Maintenance Tools and Supplies
Having the right tools makes maintenance easier and more effective.
- Soft cloths
- Compressed air
- Screwdrivers
- Spare propellers
Safe Storage Practices
Proper storage protects the drone from damage and ensures its readiness for the next flight.
- Store the drone in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight and extreme temperatures.
- Use a protective case or bag to prevent scratches and damage during transport.
- Store batteries separately in a designated battery storage case.
Regular Drone Maintenance Checklist
A regular maintenance checklist ensures consistent care and prolongs the drone’s lifespan.
- Weekly: Inspect for physical damage, clean the drone.
- Monthly: Check battery health, calibrate the compass and GPS.
- Quarterly: Perform a thorough inspection of all components, lubricate moving parts (if necessary).
Advanced Drone Techniques
Advanced techniques, such as waypoint navigation and autonomous flight, enhance the drone’s capabilities and efficiency. This section explores these techniques and their applications.
Waypoint Navigation and Autonomous Flight
Waypoint navigation allows pre-programming a flight path, while autonomous flight enables the drone to execute pre-defined maneuvers without constant manual control. These features increase efficiency and precision.
Drone Software and Applications
Specialized software and apps provide advanced control and features for drones, including flight planning, data analysis, and camera control.
Different Flight Modes
Various flight modes offer different levels of control and autonomy, catering to various needs and skill levels.
| Feature | Description | Benefits | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Waypoint Navigation | Pre-programmed flight path. | Increased efficiency, precise flight paths. | Requires careful planning, potential for errors. |
| Return-to-Home (RTH) | Drone automatically returns to its takeoff point. | Safety feature, simplifies operation. | Relies on GPS signal, may not be accurate in challenging conditions. |
| Follow Me | Drone automatically follows a designated subject. | Convenient for filming moving subjects. | Requires a strong GPS signal, may struggle with fast-moving subjects. |
Successfully operating a drone involves a blend of technical skill, careful planning, and a deep respect for safety regulations. By following the steps Artikeld in this guide, you’ll be well-prepared to take to the skies responsibly and confidently. Remember, continuous learning and practice are key to becoming a proficient and safe drone pilot. So, get ready to explore the world from a whole new perspective!
Helpful Answers: How To Operate A Drone
What type of drone is best for beginners?
User-friendly drones with GPS stabilization and automatic return-to-home features are ideal for beginners. Look for models with intuitive controls and good flight stability.
How long does a drone battery typically last?
Drone battery life varies depending on the model and flight conditions. Expect flight times ranging from 15 to 30 minutes, but always check your specific drone’s specifications.
What should I do if I lose the GPS signal?
If you lose GPS signal, your drone may enter a failsafe mode and attempt to return to its takeoff point. If this doesn’t happen, carefully bring it down manually, prioritizing a safe landing.
How often should I calibrate my drone’s compass?
Calibrate your drone’s compass before each flight, especially if you’re in an area with significant magnetic interference. Consult your drone’s manual for specific instructions.